[Surface treatment] About Electrodeposition

In the surface treatment industry, people often mention "electrodeposition." What is it? Electrodeposition is a coating technology that uses an electric field to cause a charged coating to migrate directionally through a water-based medium and adhere to the surface of a conductive substrate. Another common term is "electrophoretic coating," which is the same process, just with a different name.
Electrodeposition coating principle
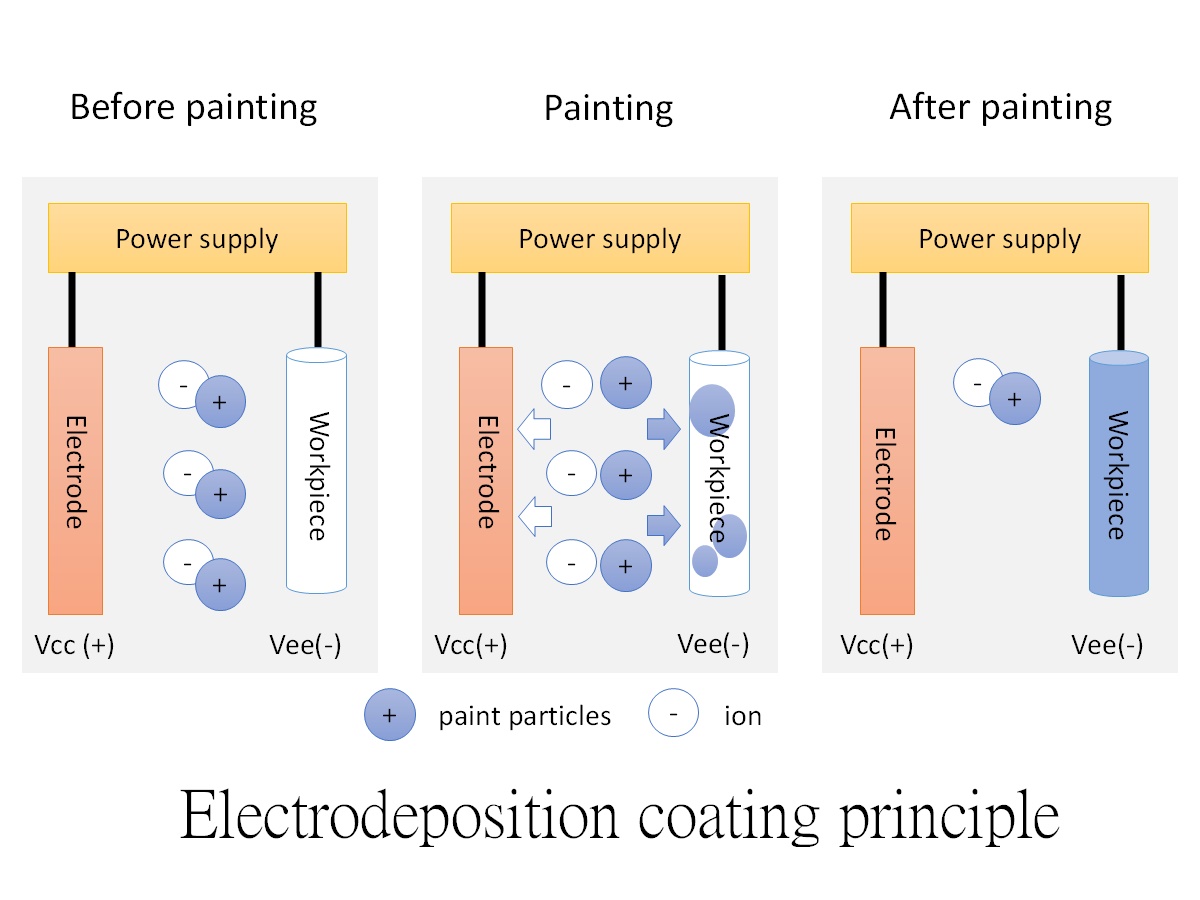
- Before painting
Before the power supply is powered on, ions carry paint particles and remain suspended in the workspace.
- During painting
When the power supply is powered on, the electrode becomes positive and the workpiece becomes negative. Due to their respective properties, paint particles and ions migrate to the electrode and workpiece.
- After painting
Once sufficient adsorption has reached the workpiece surface, adsorption ceases, leaving only paint particles and ions floating in the workspace. The coating adsorption process resumes when a new workpiece is placed.
Advantages and disadvantages of electroplating
Advantages of electroplating
- Excellent Rust and Corrosion Resistance: Electrodeposition coatings offer strong adhesion, effectively enhancing the rust and corrosion resistance of workpieces, even protecting inner layers and crevices.
- Uniform Coating Coverage: Using electric current, coatings can be evenly deposited onto conductive surfaces, including complex interior surfaces, corners, and hidden areas, achieving a complete, gap-free coating.
- High Efficiency and Low Cost: Electrodeposition coating is highly automated, allowing for the recycling and reuse of undeposited coatings. This results in a nearly 100% coating utilization rate, significantly reducing material waste and manufacturing costs.
- Environmental and Safety: Water-based coatings have low volatile organic compound (VOC) content, resulting in lower emissions and compliance with environmental regulations. Water-based coatings also pose a lower fire risk than solvent-based coatings.
- Smooth and Beautiful Surface: Electrodeposition coatings produce smooth, beautiful coatings with minimal defects such as paint flow and blistering, enhancing the product's aesthetic quality.
- Easy to Control Coating Thickness: Electrodeposition coatings allow for precise control of coating thickness and uniformity.
Disadvantages of electroplating
- Substrate Conductivity Requirements: Electrodeposition coating utilizes electric current and is therefore only suitable for conductive materials (such as metals), not non-conductive materials.
- Initial Equipment Investment: While the initial cost of using electrodeposition equipment is low, the initial cost of setting up fully automated electrodeposition equipment is high.
- Sensitivity to Operating Conditions: Coating quality is affected by numerous factors, such as power supply, temperature, and current, requiring precise control to avoid uneven film thickness and other defects.
- Coating Thickness Compared to Other Anti-Corrosion Coatings: Electrodeposition coatings can achieve thinner film thicknesses than some heavy-duty corrosion-resistant coatings (such as powder coatings), requiring careful evaluation based on application requirements.
Summarize
Electrodeposition coating plays an indispensable role in surface treatment applications, especially for workpieces where surface appearance is paramount. It can achieve superior color uniformity and coating thickness. Coupled with its nearly 100% coating utilization rate, environmental protection, and low cost advantages, electrodeposition coating will be a long-term process relied upon by the surface treatment industry.
